Market Entry Strategies take the spotlight in this exploration of expanding businesses into new territories. Get ready to dive into the world of strategic planning and growth!
Market Entry Strategies Overview
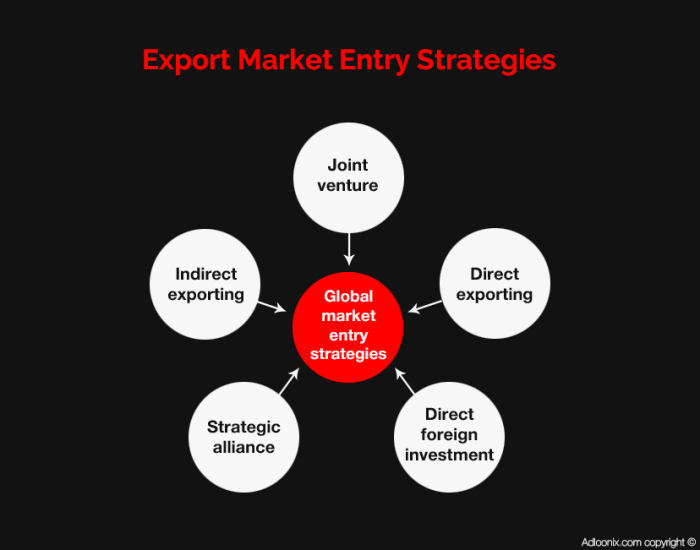
Exploring market entry strategies is essential for businesses looking to expand into new territories. These strategies help companies determine the best approach to enter a new market and establish a strong presence.
Types of Market Entry Strategies
- Exporting: Selling products or services to a foreign market without establishing a physical presence.
- Licensing: Allowing a foreign company to use your intellectual property in exchange for royalties.
- Franchising: Granting the rights to use your business model and brand to a third party in a foreign market.
- Joint Ventures: Partnering with a local company to enter a new market and share resources and risks.
- Direct Investment: Establishing a physical presence in a foreign market through wholly-owned subsidiaries or acquisitions.
Importance of Selecting the Right Market Entry Strategy
Choosing the right market entry strategy is crucial for the success of a business in a new market. It can impact factors such as market penetration, profitability, risk management, and long-term sustainability. By carefully evaluating the market conditions, competition, regulations, and resources, companies can select the most suitable strategy to achieve their goals and maximize growth potential.
Exporting as a Market Entry Strategy
Exporting is a market entry strategy where a company sells its products or services in a foreign market. This involves shipping goods or providing services to customers in another country, either directly or through intermediaries.
Advantages of Exporting
- Access to a larger market without the need for a physical presence
- Lower investment costs compared to other market entry strategies like setting up subsidiaries
- Ability to capitalize on economies of scale
- Diversification of revenue streams
Disadvantages of Exporting
- Risk of trade barriers and tariffs
- Dependence on intermediaries for distribution
- Cultural and language barriers
- Logistical challenges and longer lead times
Companies Successfully Using Exporting
- Apple: Apple exports its products globally, reaching customers in various countries through its online store and authorized resellers.
- Nike: Nike exports its athletic footwear and apparel to markets worldwide, leveraging its strong brand presence.
- Starbucks: Starbucks has successfully exported its coffee products to numerous countries, adapting to local tastes and preferences.
Licensing and Franchising: Market Entry Strategies
Licensing and franchising are both popular market entry strategies used by companies to expand globally. While they may seem similar, there are key differences between the two approaches.
Difference between Licensing and Franchising
Licensing involves giving another party the right to use intellectual property, such as trademarks, patents, or technology, in exchange for a fee or royalty. The licensee does not have as much control over the business operations and is mainly focused on using the licensed property. On the other hand, franchising allows the franchisee to use the entire business model, including trademarks, products, and services, in exchange for a franchise fee and ongoing royalties. Franchisees have more control over the day-to-day operations compared to licensees.
Key Considerations when Choosing between Licensing and Franchising
- Control: Franchising offers more control over operations compared to licensing.
- Investment: Licensing generally requires less initial investment compared to franchising.
- Brand Image: Franchising helps maintain brand consistency and image, while licensing may vary depending on the licensee.
- Operational Support: Franchisees receive more support and guidance from the franchisor compared to licensees.
Examples of Global Expansion through Licensing or Franchising
- McDonald’s: McDonald’s has expanded globally through franchising, allowing local operators to run individual restaurants while maintaining the brand’s standards and quality.
- Disney: Disney has successfully used licensing to expand its brand globally, allowing various companies to produce merchandise, movies, and other products using Disney characters.
Joint Ventures and Strategic Alliances
Joint ventures and strategic alliances are effective market entry strategies that companies use to expand their reach and capabilities in new markets. By forming partnerships with other businesses, companies can leverage each other’s strengths and resources to enter new markets more efficiently.
Benefits and Challenges of Joint Ventures
- Benefits:
- Shared resources and expertise
- Risk-sharing
- Access to new markets
- Challenges:
- Potential conflicts between partners
- Loss of decision-making control
- Sharing profits with partners
Benefits and Challenges of Strategic Alliances
- Benefits:
- Access to complementary resources
- Cost savings through shared expenses
- Risk mitigation
- Challenges:
- Dependence on partner’s performance
- Confidentiality concerns
- Potential for conflicts of interest
Examples of Successful Joint Ventures and Strategic Alliances
One notable example of a successful joint venture is Sony Ericsson, a partnership between Sony and Ericsson to produce mobile phones. This collaboration allowed both companies to combine their expertise in electronics and telecommunications, leading to the development of innovative products.
As for strategic alliances, the partnership between Starbucks and Nestle is a prime example. Nestle gained access to Starbucks’ premium coffee products, while Starbucks expanded its distribution channels globally. This alliance benefited both companies by tapping into each other’s strengths.